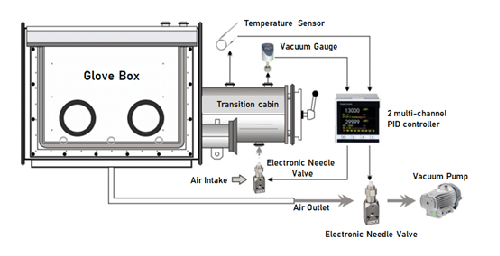
A Detailed Tutorial on Vacuum Degree and Temperature Control Method in Glove Box
Abstract: In order to reach powerful functions of glove box for two environmental variables of vacuum and temperature in glove box. This article focuses on integrated solution for accurate measurement and control of vacuum and temperature, and describes the upstream, downstream, bi-directional methods. Also introduces the specific application of switching control mode in different vacuum degree ranges, and demonstrates the new proportional flow control valve and 24-bit ultra-high-precision PID controller used in the control.
1. Questions
Vacuum glove boxes are often used for readily oxidizable and deliquescent substances. Chemical reactions, material processing and performance testing that require manual operations in an anaerobic and anhydrous environment are very helpful. The core function of glove box is to provide a vacuum environment and easy to use, but in current practical applications most glove boxes only use anaerobic environment and manual operation functions of glove box, and do not give full capacity to the role of glove box. The more powerful application of glove box is also reflected in the following two aspects:
(1) The vacuum glove box is a hermetic environmental box, and the ultimate vacuum degree can generally reach about 10Pa, so that vacuum degree in glove box can be controlled at any set point between 10Pa and atmospheric pressure as required. Various chemical reactions, experiments and tests that are sensitive to vacuum can be carried out; also various manual operations can be carried out without changing and destroying the vacuum environment.
(2) In addition to vacuum, temperature is another important environmental variable for many reactions, experiments and tests. By placing the corresponding heating device in the glove box, various experimental studies under the combined environment of temperature and vacuum degree can be carried out. And so on, other physical quantity environmental conditions can also be configured to form multi-physical quantity coupling test conditions under various boundary conditions. In order to achieve the full performance of a vacuum glove box, it focuses on two environmental variables of vacuum degree and temperature in the glove box. This article introduces in detail the integrated solution for accurate measurement and control of vacuum degree and temperature, and introduces the different vacuum degree ranges of upstream, downstream and bidirectional control modes in vacuum control process.
2. Vacuum control in glove box
Glove box belongs to a low vacuum environment cavity. The vacuum degree of the glove box using a mechanical pump can generally reach an absolute pressure of about 10Pa. By vacuuming and filling with inert gas, the vacuum degree of the glove box can be controlled from 10Pa to one atmosphere (absolute pressure 0.1MPa). For control in such a vacuum range spanning four orders of magnitude, vacuum sensors with different precisions will be used according to actual needs, and there will be different control modes accordingly. The following is the specific content of each control mode.
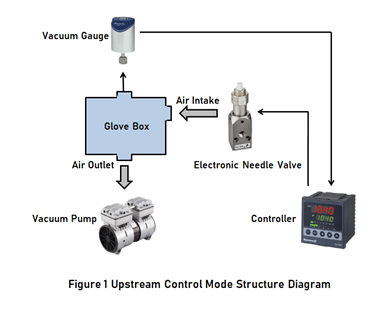
2.1 Upstream Control Mode
As shown in Figure 1, under the condition that the pumping speeds of downstream vacuum pump is kept constant. The upstream control mode is to adjust the opening of proportional flow control valve of upstream air intake port through PID vacuum pressure controller according to the measurement signal of vacuum gauge, that is, by controlling intake flow to keep pressure in glove box at the set point. Upstream mode is often used for high vacuum control.
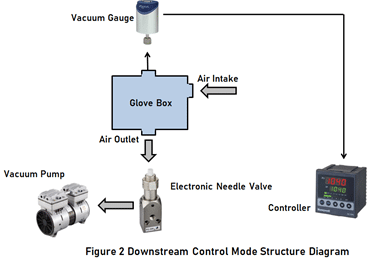
2.2 Downstream Control Mode
As shown in Figure 2, under the condition that the pumping speed of downstream vacuum pump is kept constant, the downstream control mode is to adjust the opening of proportional flow control valve of downstream air outlet through PID vacuum pressure controller according to the measurement signal of vacuum gauge, that is, by controlling the air flow rate, the pressure in glove tank is controlled at the set value. We can see that downstream mode is often used for low vacuum control.
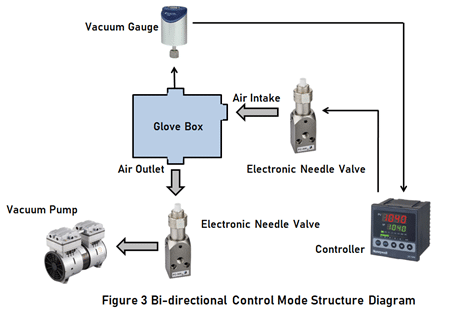
2.3 Bi-directional Control Mode
The above upstream and downstream control modes have their own advantages, and are rarely used alone in practical applications. Generally, the upstream and downstream modes are integrated together, which is the so-called bi-directional control mode, as shown in Figure 3. In bi-directional control mode, the vacuum pressure controller is required to have forward and reverse control functions, that is, reverse control for upstream proportional flow control valve and reverse control for downstream proportional flow control valve.
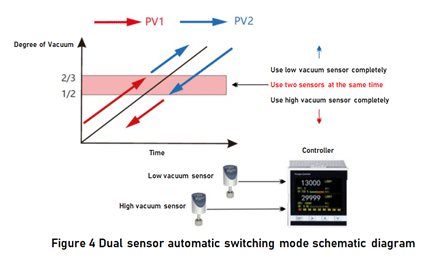
2.4 Dual sensor automatic switching mode
As mentioned above, if the accurate measurement and control of vacuum degree is carried out in the full range of 10Pa~0.1MPa, it is generally necessary to configure two high-precision diaphragm pressure gauges of 1000Torr and 10Torrswitch automatically. As shown in Figure 4, the high switching point (2-3) is the high point where low vacuum sensor works, and the low switching point (1-2) is the low point where high vacuum sensor works. The controller performs smoothing calculation between these two points. When the continuous sampling of low vacuum measurement PV1 and high vacuum measurement PV2 is below the lower switching point, switching to the rough vacuum sensor. When continuous sampling of low vacuum measured value PV1 and high vacuum measured value PV2 is above the upper switching point, the switch to high vacuum sensor is made.
3. Selection of vacuum gauge, valve and controller
3.1 Selection of vacuum sensor
Like other sensors, various vacuum sensors also have a certain measurement range and accuracy. The basic rule is that a sensor with a wide measurement range has poor accuracy; a sensor with high measurement accuracy has a narrower measurement range. For glove box, as shown in Figure 5, the used vacuum sensors generally have the following three categories:
(1) Conventional vacuum gauge: Pirani vacuum gauge, the accuracy is ±(15~50)% of the full scale, but one vacuum gauge can cover the full scale.
(2) High-precision vacuum gauge: diaphragm pressure gauge, the accuracy is ±2.5% of the full scale, if it covers the range of 10Pa~0.1MPa, two vacuum gauges of 1000Torr and 10Torr are generally required.
(3) Ultra-high precision vacuum gauge: semiconductor vacuum gauge, the accuracy is ±0.05% of the full scale, and the effective range is 50Pa ~ 0.1MPa, which cannot cover higher vacuum.
3.2 Selection of electric valve
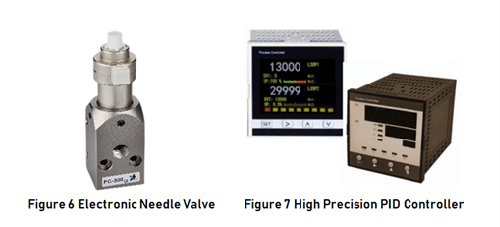
In glove box of vacuum control, two types of valves are generally involved: one is an air intake valve that adjusts the flow at air intake, and the other is an exhaust valve that adjusts the exhaust flow. Air intake valves are mostly used for small flow regulation, so needle valves are generally selected. Exhaust valves are mostly used for vacuuming, so ball valves with larger diameters are generally required. Due to the automatic control, both needle valves and ball valves are required to be driven by DC voltage, DC current or digital signal (RS485) which is the so-called proportional flow control valve. Proportional flow control valve selects a small-sized stepper motor-driven proportional flow control valve, as shown in Figure 6. This proportional flow control valve has high response speed (within 1s) and linearity (within 1%). For FC series proportional flow control valve, please visit https://www.genndih.com/proportional-flow-control-valve.htm
3.2 Selection of controller
From the above various control modes of vacuum degree of glove box, it can be seen that control process of vacuum degree puts forward high requirements for the controller. As shown in Figure 7, the selected controller must meet the following criteria:
(1) At least it is a PID controller, and has the function of PID parameter self-tuning.
(2) The accuracy of vacuum gauge itself is high. In order to give full play to the measurement accuracy of vacuum gauge, PID controller that needs data acquisition and control must have high accuracy. It is recommended that controller should be 24-bit A/D acquisition and 16-bit D/A output. (3) At least 2 channels are required to achieve simultaneous measurement and control of temperature and vacuum degree, also to reduce installation space.
(4) Multiple input signal access functions, which can directly connect the input signals of different types of sensors such as thermocouple, thermal resistance, DC voltage, etc., to achieve simultaneous testing, display and control of different parameters.
(5) Forward and reverse control function to reach two-way control mode.
(6) With dual sensor switching function, each channel can support dual sensor switching of high and low temperature and high and low vacuum. Two channels can form a control combination with a total of four sensors connected.
(7) Program control function, you can create and save multiple control programs by yourself, and you only need to select and call to start (program control mode).
(8) It has a communication interface to connect with computer, such as the RS485 interface of the standard MODBUS protocol.
4. Temperature control of the glove box
In addition to providing a vacuum environment, the glove box can also put a heating device in the glove box to perform various experiments and tests at different temperatures, so it is necessary to introduce temperature control function into glove box application. Temperature control is a very mature and classic technology, which is generally realized by using a PID controller in combination with a temperature sensor. In order to reduce the cost and installation volume, a multi-channel PID controller is generally used to control temperature and vacuum degree at the same time. The controller communicates with a computer to display and store measurement control data and curves. The working temperature in glove box is generally not required to be too high, but if thermal protection and cooling are done well, the working temperature range above 1000°C can also be achieved. The temperature measurement sensor generally chooses a thermocouple. If the measurement accuracy is high, the thermal resistance and the thermistor temperature sensor can also be selected. These sensors can be directly connected to the above-mentioned high-precision PID controller.
5. Conclusion
Through the introduction of above content, the various control methods of vacuum degree and temperature in glove box and the main sensors, proportional flow control valve and PID controllers involved are basically explained. In specific applications, partial improvements can be made to the specific structure and function of glove box, and the overall design, installation and integration of glove box can also be carried out according to actual requirements.
Although this article only introduces the measurement and control of vacuum degree and temperature in glove box, these methods and specific implementation contents can also be extended and applied to the control of test parameters in other fields that are more sensitive to the atmosphere environment, such as low temperature, geometric quantity, optics and acoustics.